When it comes to security compliance, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF) has built a reputation for effectively guiding organizations toward achieving cyber resilience. NIST CSF stands out for its unique approach to risk management, focusing on cybersecurity outcomes instead of rigid requirements and establishing a flexible framework that organizations can tailor to their distinct needs. In this article, we will explore the components and benefits of the NIST CSF and break down its core functions to outline different best practices that organizations can adopt to build a robust security program.
Overview of NIST CSF
Published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST CSF provides guidelines for managing risks through a classification of high-level cybersecurity outcomes that organizations can seamlessly align with their security considerations, technology implementation, and business objectives. The framework is divided into three main components: the Core, Organizational Profiles, and Tiers.
The CSF Core organizes these cybersecurity outcomes into 6 Functions: Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Each function is further arranged into categories and subcategories that detail specific, actionable outcomes that organizations can fulfill to ensure effective risk management.
Meanwhile, the CSF Organizational Profiles consist of steps on how an organization can identify and understand its Current Profile or existing cybersecurity posture, as well as its Target Profile or the cybersecurity outcomes it aims to achieve through the NIST CSF. Finally, the CSF Tiers describe different levels of cybersecurity implementation: Partial, Risk-informed, Repeatable, and Adaptive, which organizations can use to inform their organizational profiles.

How does NIST CSF benefit organizations?
The NIST CSF is designed to help organizations effectively address their unique risks regardless of size, sector, or security maturity, and develop strong risk management and governance practices to foster sustainable growth. It supports different aspects of an organization’s risk management strategy, including:
- Cybersecurity readiness: The NIST CSF categories and subcategories provide a range of controls, including access control, awareness and training, and continuous monitoring, which organizations can implement to safeguard their digital infrastructure and data from various threats and improve overall cybersecurity.
- Regulatory compliance: Risk assessment, incident reporting, and safeguarding the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data are some of the security measures specified in NIST CSF that align with the requirements of regional laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, and sector-specific regulations such as the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). NIST CSF also shares similar provisions with other cybersecurity standards such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2. By adopting NIST CSF, not only do organizations streamline their compliance with legal and regulatory requirements but also enhance their capability to meet industry standards for data privacy and security.
- Operational resilience: With a cybersecurity risk management framework that enables your organization to effectively identify, prioritize, mitigate, and monitor risks, you can minimize and prevent security incidents and disruptions that can significantly impact your assets, operations, or reputation, ensuring business continuity.
In addition, implementing the NIST CSF saves organizations considerable time, effort, and resources on damage control by eliminating or reducing the possibility of risks materializing.
NIST CSF best practices
The 6 core functions of the NIST CSF make up a list of categories that define specific outcomes, helping organizations put in place processes and security measures to strengthen their cybersecurity risk management strategy. Each outcome represents each of the best practices within the framework:
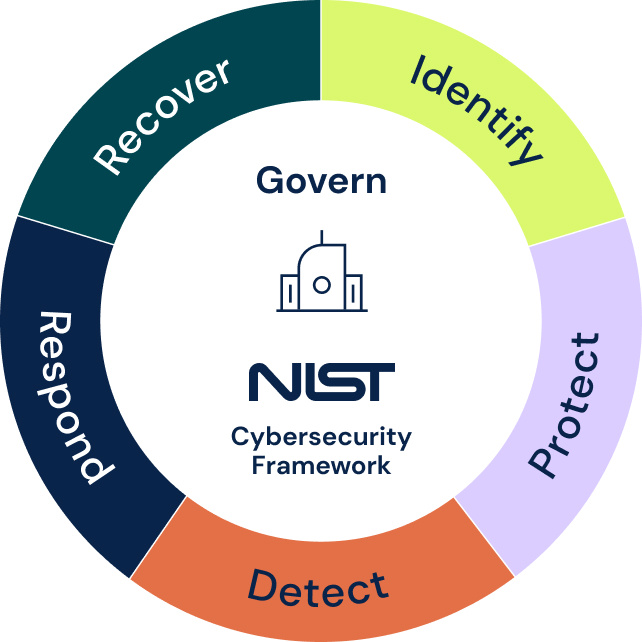
Govern
An overarching function that makes all other functions of the NIST CSF work, Govern encompasses the establishment of the organization’s cybersecurity risk management strategy and policies. This involves examining the organization’s business environment, assigning roles and responsibilities to key personnel, and ensuring oversight and clear communication of all risk management activities across the entire organization. The Govern function also includes integrating cybersecurity supply chain risk management into the organization’s broader enterprise risk management strategy.
There are six outcomes produced during the Govern phase:
|
Category |
Outcome |
|
Organizational Context |
Define the organization’s mission, legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements, stakeholder expectations for risk management, and other dependencies |
|
Risk Management Strategy |
Determine the organization’s risk tolerance and risk appetite and establish risk management processes |
|
Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities |
Assign roles, responsibilities, and authorizations to executive leadership and staff and allocate resources for risk management |
|
Policy |
Enforce a risk management policy across the organization |
|
Oversight |
Monitor risk management activities |
|
Cybersecurity Supply Chain Risk Management |
Establish cybersecurity supply chain risk management processes, roles and responsibilities, and policy |
Identify
Next, the Identify function enables the organization to develop a deep understanding of its assets —hardware, software, facilities, services, data, systems, and human resources —as well as the equivalent risks that can impact them. This helps the organization align its risk management efforts with its established mission and risk management strategy. During this stage, the organization can also conduct activities to identify improvements to its risk management processes, procedures, and policies.
The Identify function has 3 outcomes:
|
Category |
Outcome |
|
Asset Management |
Identify all assets of the organization and determine which should be prioritized for risk management |
|
Risk Assessment |
Identify vulnerabilities and threats, assess their likelihood and impact to inform prioritization, and formulate a risk response |
|
Improvement |
Identify improvements to the organization’s risk management strategy by performing tests and evaluating current processes and procedures |
6clicks can help you streamline this stage through our powerful risk management and asset management features. Take advantage of turnkey risk libraries to expedite risk identification. Use our comprehensive risk register with custom fields and workflows and automated risk scoring to simplify your risk assessments. Create risk treatment plans and leverage integrated task management features to assign and track remediation efforts. Meanwhile, 6clicks’ Assets Register enables you to store and organize your assets within a single register and link them to their associated risks for enhanced management and monitoring.
Protect
In this phase, security measures or controls are implemented to safeguard the assets as well as mitigate the risks that were identified and prioritized from the previous function. Outcomes of the Protect function include:
|
Category |
Outcome |
|
Identity Management, Authentication, and Access Control |
Protect critical data and assets by restricting access to authorized users, services, and devices |
|
Awareness and Training |
Protect critical data and assets by equipping relevant personnel with knowledge and skills to perform their duties |
|
Data Security |
Protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data being stored, used, or transmitted through measures such as encryption and backups among others |
|
Platform Security |
Protect critical data and assets by maintaining and monitoring systems and infrastructure |
|
Technology Infrastructure Resilience |
Protect critical assets and strengthen organizational resilience through the development and management of a robust security architecture |
With 6clicks’ control management functionality, you can implement administrative controls such as an acceptable use policy and security awareness programs, as well as technical controls like multi-factor authentication, patch management, firewalls, endpoint protection, and network segmentation to fulfill the outcomes of this function.
Detect
On the other hand, the goal of the Detect function is to facilitate the timely identification and analysis of anomalies, threat indicators, and potential threat events to enable the detection of cybersecurity attacks and incidents as they occur. This function has two significant outcomes:
|
Category |
Outcome |
|
Continuous Monitoring |
Detect anomalies, threat indicators, and potential threat events by monitoring assets using surveillance tools and alerting systems |
|
Adverse Event Analysis |
Detect the occurrence of cybersecurity incidents by analyzing the impact and scope of anomalies, threat indicators, and potential threat events |
For this phase, you can utilize technologies such as Threat Detection and Response (TDR) tools and set up controls using 6clicks. Ensure the effectiveness of your controls through our Continuous Control Monitoring feature that enables automated control testing and real-time alerts for control failures and security incidents.
Respond
During the Respond stage, actions are taken to reduce the impact of detected incidents. Details of the incident and what actions were taken to resolve it are also communicated to internal stakeholders such as employees and board members, as well as reported to external stakeholders like government authorities as part of the organization’s legal or regulatory obligations. The Respond function supports the following outcomes:
|
Category |
Outcome |
|
Incident Management |
Respond to cybersecurity incidents through the development, execution, and management of an incident response plan |
|
Incident Analysis |
Ensure effective incident response by conducting incident investigation and root cause analysis |
|
Incident Response Reporting and Communication |
Ensure incident information and response activities are communicated to internal and external stakeholders |
|
Incident Mitigation |
Contain or eliminate incidents by ensuring incident response activities are performed |
6clicks’ incident management functionality can equip your organization with a built-in incident register for storing, categorizing, and managing incidents, as well as custom incident reporting forms to enable comprehensive incident capture and analysis. Assign remediation tasks to team members and leverage automated workflows and updates powered by our Jira integration to optimize your incident response activities.
Recover
Lastly, this function deals with the timely restoration of assets and operations impacted by a cybersecurity incident. It includes executing the recovery portion of the incident response plan, restoring normal operating conditions, verifying the integrity of restored assets, and reevaluating and adjusting the organization’s cybersecurity risk management strategy to establish new operating procedures after recovering from an incident. The Recover function is broken down into two outcomes:
|
Category |
Outcome |
|
Incident Recovery Plan Execution |
Recover the availability of systems and services affected by the cybersecurity incident through restoration activities |
|
Incident Recovery Communication |
Restoration activities are communicated to internal and external stakeholders |
Automate NIST CSF compliance with 6clicks
Effortlessly implement these best practices with our NIST CSF solution. Download the framework for free along with ready-to-use NIST CSF control sets and assessment templates to streamline your compliance. Get in touch with a 6clicks expert to get started!
Frequently asked questions
Is the NIST CSF mandatory?
According to Executive Order 13800, compliance with the NIST CSF is mandatory for government departments and agencies to improve cybersecurity in the US government and safeguard federal information and critical infrastructure. For other organizations, implementing the NIST CSF is voluntary.
How many controls does NIST CSF have?
The NIST CSF has 22 categories and 106 subcategories or controls, distributed across its 6 core functions.
What are the NIST CSF best practices?
Conducting governance activities to guide the execution of your risk management strategy, identifying your organization’s assets and risks, putting in place security measures to protect those assets and address those risks, detecting potential threat events to get ahead of cybersecurity incidents, responding to these incidents, and recovering affected assets and operations—make up the NIST CSF best practices.
Written by Jami Samson
Jami is a seasoned Technical Writer at 6clicks, where she harnesses her extensive experience in domains such as information technology, artificial intelligence, and GRC to craft high-quality content. Having worked in the marketing field since 2017, she has established a solid background in copywriting and content writing and is skilled in translating complex topics into informative and engaging pieces. Apart from writing, Jami is also passionate about music.









