As the regulatory landscape expands and cyber threats evolve in response to an increasingly digital world, organizations depend on various disciplines to safeguard their data and address risks. Security, compliance, and assurance are terms that often coincide and are used by organizations to define their strategies for protecting their assets, systems, and business. However, understanding the nuances between these concepts can help an organization find a solution that best aligns with their needs and empowers them to effectively navigate the dynamic digital landscape. Let’s discuss the meaning of security, compliance, and assurance and clarify their distinctions:
What is security, compliance, and assurance?
Security refers to practices, policies, procedures, and controls an organization implements to safeguard its data, assets, systems, and operations against unauthorized access, misuse, disclosure, alteration, destruction, or disruption. It covers combating diverse threats, from physical threats such as natural disasters to digital and cyber threats like data breaches and malware attacks. Security also serves as an umbrella term for other disciplines such as:
- Cybersecurity, which encompasses preventing, detecting, and responding to cyberattacks on an organization’s devices, networks, and systems,
- Information security, which aims to protect all forms of information including sensitive data and assets through risk mitigation, and
- IT security, which focuses on securing the technology infrastructure of organizations, including physical facilities
Meanwhile, compliance is the process of meeting legal and regulatory requirements that apply to an organization’s operations, processes, and activities. In the context of security, regulatory compliance is the adherence to laws, standards, and regulations specific to an industry or jurisdiction, while security compliance involves abiding by security frameworks, policies, and standards for safeguarding data, assets, systems, and operations.
Assurance, on the other hand, relates to the confidence, trust, and certainty that stakeholders, customers, or regulators have in the effectiveness, reliability, and integrity of an organization's security and compliance measures. To achieve compliance assurance, organizations must continuously assess, maintain, and address non-conformities in their security controls and processes. This means updating security policies and controls according to audit and assessment findings, new threats, and changes in regulations. Audit and compliance reports and documents detailing an organization’s policies and procedures are also essential records that support compliance assurance.
Bringing everything together, security is concerned with upholding internal policies for data protection and privacy, while compliance is centered around meeting external requirements dictated by legislation and regulatory bodies, and assurance validates the effectiveness of both security and compliance practices within an organization.
Similarities between security, compliance, and assurance
Though each has a distinct focus, security and compliance can be compared to each other, as both aim to provide a structure for an organization’s defenses against potential threats through risk management. Similarly, compliance and assurance offer organizations the same benefits of demonstrating their capacity for robust security and enhancing their credibility. Here are other ways that security, compliance, and assurance align:
- Shared objectives – Security, compliance, and assurance all ensure the integrity of systems and infrastructure in order to safeguard an organization and its data, assets, operations, and stakeholders.
- Adherence – Each discipline involves adhering to internal policies, industry standards, legal obligations, and regulatory requirements through the implementation of controls, processes, and procedures.
- Focus on governance – Governance is a common theme in all three disciplines as they all involve establishing rules, controls, and oversight mechanisms to ensure that operations are conducted in a secure, compliant, and reliable manner.
- Integration with business objectives – While security, compliance, and assurance are often viewed as technical or regulatory functions, they are ultimately aligned with the broader business objectives of an organization. They help safeguard the organization's assets, maintain compliance with regulations, and build trust with stakeholders, which in turn supports the achievement of business goals.
- Role of monitoring, assessment, and improvement – Monitoring, assessment, and continuous improvement are essential components of security, compliance, and assurance efforts. This includes monitoring for security incidents and non-compliance, conducting regular audits and assessments to evaluate security effectiveness and compliance status, and continuously enhancing security and compliance processes and practices to maintain assurance.
Security vs compliance vs assurance: What are the differences?
Despite their similarities, one does not equal the other. Compliance needs may be fulfilled by an organization’s security measures, but being compliant does not necessarily mean being secure. At the same time, compliance alone does not guarantee assurance. To better illustrate the differences between security, compliance, and assurance, here is an overview of the components of each discipline:
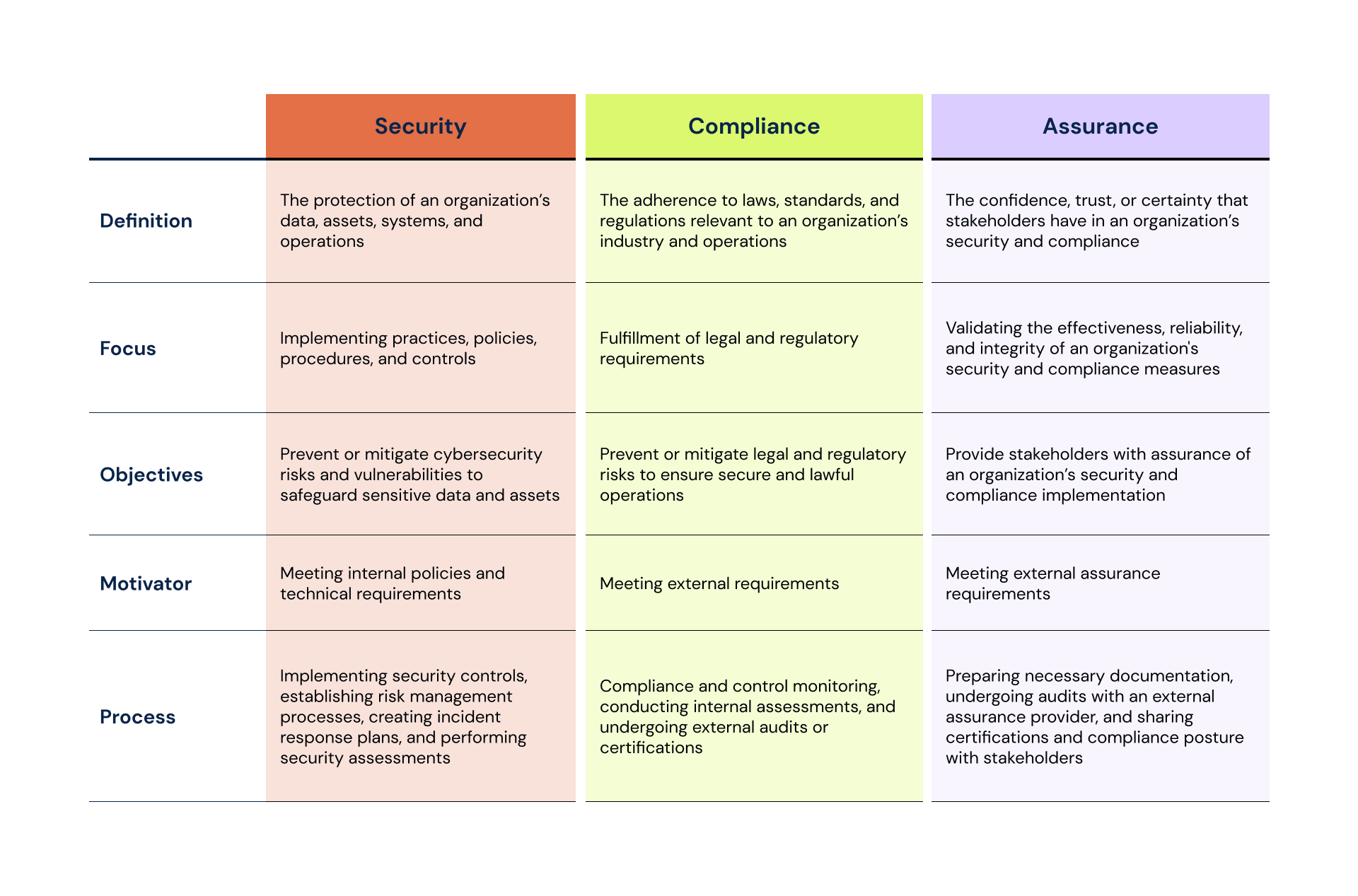
Overall, security, compliance, and assurance may differ in scope and methods, but they are interconnected disciplines that work together to protect and enhance an organization’s resilience.
Bolster security, ensure compliance, and achieve assurance with 6clicks
6clicks’ Security Compliance solution empowers your organization to demonstrate compliance with various regulatory and security frameworks such as DORA, NIST CSF, ISO 27001, CMMC, and more.
Simplify compliance management by using 6clicks’ turnkey policy and control sets or create and manage your own security policies and controls and assign tasks to key personnel to track and measure their performance. 6clicks’ AI engine, Hailey can also automate compliance mapping, policy gap analysis, and generating assessment responses to streamline your compliance process.
Meanwhile, with 6clicks’ IT Risk Management and Issues and Incident Management features, your organization can leverage comprehensive risk and issue registers, custom workflows and incident submission forms, and intuitive reporting tools to identify, organize, and remediate risks and issues, facilitate risk assessment and incident reporting, and gain powerful insights to inform your security and compliance strategies.
Finally, utilize 6clicks’ Audit & Assessment functionality with built-in templates to become audit-ready and achieve assurance for your organization’s security and compliance capabilities.
Learn more about 6clicks’ integrated, AI-powered security compliance and risk management platform below:
Frequently asked questions
How do security, compliance, and assurance relate to one another?
In essence, security protects an organization’s data, assets, systems, and operations from potential threats, while compliance provides frameworks and requirements for security through laws, standards, and regulations that organizations must adhere to. Assurance, on the other hand, verifies an organization’s security and compliance and fosters stakeholder trust.
What are some examples of compliance requirements?
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is an example of a regulatory framework that provides mandatory security and compliance requirements for European financial institutions, which includes ICT risk management, incident reporting, operational resilience testing, and third-party risk management.
What is the process for obtaining external assurance?
Before going through an external audit with an assurance provider, organizations must prepare documentation detailing their security policies, controls, and procedures as well as evidence of their compliance in the form of internal audit and assessment reports.
Written by Louis Strauss
Louis is the Co-founder and Chief Product Marketing Officer (CPMO) at 6clicks, where he spearheads collaboration among product, marketing, engineering, and sales teams. With a deep-seated passion for innovation, Louis drives the development of elegant AI-powered solutions tailored to address the intricate challenges CISOs, InfoSec teams, and GRC professionals face. Beyond cyber GRC, Louis enjoys reading and spending time with his friends and family.









