In the age of artificial intelligence, not only can algorithms define our digital experiences and influence business decisions, but they are also instrumental in our social development and economic growth. With the immense raw power that AI holds, governments and organizations must commit to practicing responsible AI and guarantee its use for the greater good. Let’s explore in depth the significance of responsible AI, its key principles, and successful applications of responsible AI by various tech firms as well as the steps that organizations can take to uphold what it stands for.
What is responsible AI?
Responsible AI is a set of principles that govern how artificial intelligence should be used to develop and deploy AI-based products and services in compliance with laws and ethical standards. It covers a holistic approach to building trustworthy AI systems and focuses on fairness, transparency, security, and accountability.
At its core, responsible AI is about upholding human rights and values and ensuring safety for both users and developers. Organizations developing and deploying AI systems must adhere to responsible AI principles using frameworks, standards, and regulations that contain rules and requirements for AI governance.
Why is responsible AI needed?
The need for responsible AI stems primarily from the dynamic, complex, and unpredictable nature of AI technologies such as machine learning. Since they learn from human behavior and are capable of autonomous actions and decisions, the use of AI systems comes with certain risks and must therefore be managed. Now with the mass adoption and widespread use of AI, the goal of responsible AI is to promote:
Risk management
AI systems pose a variety of risks, typically those concerning privacy and security. One of the main applications of AI is collecting and processing personal and sensitive data, which can be subject to unauthorized access, misuse, and more. At the same time, AI systems are prone to vulnerabilities that can be exploited, giving rise to threats such as system manipulation and data poisoning. Responsible AI pushes organizations to establish policies and procedures to identify, prevent, manage, and treat these risks effectively.
Regulatory compliance
There are laws and regulations currently in place to support the objectives of responsible AI. Institutions such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) amongst others have determined specific requirements and best practices for the use, development, and deployment of AI systems. Achieving compliance with these regulatory frameworks and standards allows organizations to fulfill their legal obligations while delivering reliable AI solutions.
Bias mitigation
Responsible AI encompasses fairness and inclusivity and combats bias and discrimination. Since AI and machine learning models learn from real-world data, it is highly likely for them to contain biases that can lead to unfair results. For instance, an algorithm might display ads for high-paying jobs specifically to users of a particular ethnicity or gender, potentially favoring them over others. Responsible AI lays out the proper considerations that can guide organizations in developing bias-free AI systems.
What are the principles of responsible AI?

Different organizations have developed various iterations of responsible AI principles. Ultimately, it boils down to five key principles:
Fairness and inclusiveness
This principle posits that AI systems should treat everyone fairly and not show bias toward users belonging to a given demographic such as gender, race, sexual orientation, or religion. AI systems with flawed training data or algorithmic design may inadvertently perpetuate societal biases which could result in discriminatory practices. This emphasizes the need for the development of AI systems that are fair and inclusive.
To apply this principle, organizations must conduct extensive research about biases and their causes in data and build a model of fairness for different use cases and demographics before developing an AI system.
Organizations can employ inclusive design methods to understand and accommodate people from all backgrounds and develop considerations for accessibility, age, culture, language, race, gender, education, economic situation, and geographic location.
Transparency
Fostering transparency is a fundamental aspect of responsible AI. As developers, organizations must clearly define the intended outcome of the AI system, the data and algorithms used to train the model, and the logic that was applied to the data. This enables organizations to gain a better understanding of the final model that will be generated and its associated assets.
On the end-user's side, organizations must openly communicate how the AI system works, processes data, and makes decisions or predictions. Users must be able to understand which of their data will be used by the AI system and for what purpose, as well as what factors will affect the results it will produce.
Prior to development, organizations must create interpretability criteria and define which explanations are required and how they will be presented. The AI system’s behavior must also be documented at different stages of the development process.
Privacy and security
In line with the principle of privacy and security, an AI system should be capable of safeguarding private data and resisting information security attacks.
AI systems must abide by privacy laws and regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) that govern the collection, processing, and storing of data.
Organizations can ensure the protection of confidential and sensitive information by implementing an information security management system (ISMS), which comprises policies, processes, tools, and controls for identifying and responding to threats and enforcing security measures.
Reliability and safety
The principle of reliability and safety necessitates that AI systems must be dependable and operate consistently according to their intended purpose as well as respond safely in situations outside normal conditions. They must also be able to withstand intended or unintended manipulation.
Organizations must perform rigorous testing and validation to ensure that AI systems meet performance requirements and are behaving as intended under different circumstances. They must also establish a robust monitoring and tracking process to measure and maintain the AI system’s performance.
For an AI system to be safe and reliable, it must adequately respond to new situations without harming users and aim to minimize any negative impact.
Accountability
Finally, responsible AI requires organizations to take responsibility for their AI systems and maintain control over them.
Organizations must identify the roles and responsibilities of all stakeholders involved in the development of their AI systems and determine who will be accountable for ensuring compliance with legal requirements and established AI principles.
Since people’s lives and safety are at stake, the degree of autonomy of an AI system directly affects the level of accountability of the organization utilizing, developing, or deploying the AI system.
Frameworks for responsible AI
Implementing regulatory frameworks for the development of AI systems is one of the pillars of responsible AI. Regulatory frameworks ensure the ethical development and deployment of AI systems and establish firm standards for data privacy and security and the protection of individual rights. They also help solidify safety measures for the successful mitigation of risks associated with AI technologies.
Here are frameworks that organizations can use to build AI systems responsibly:
NIST AI RMF 1.0
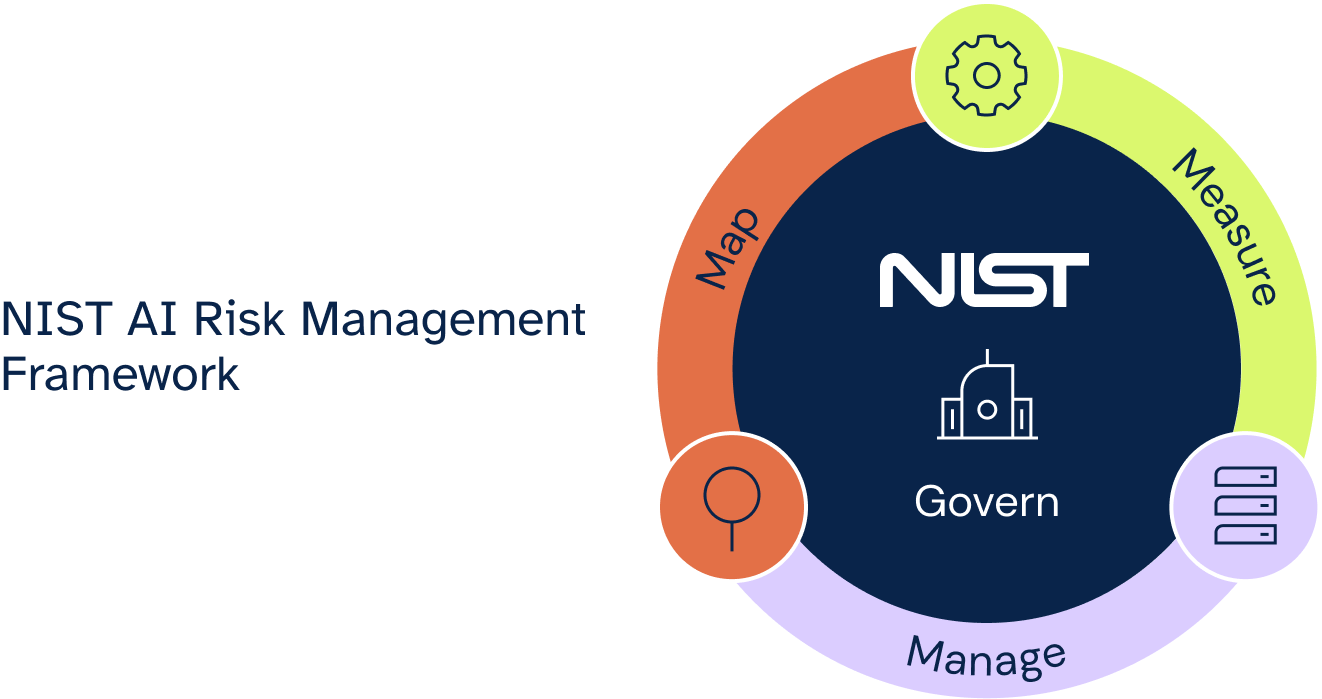
NIST’s Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework is composed of methods and practices for utilizing, developing, and deploying AI-driven products and services and enhancing the trustworthiness of AI systems to effectively manage and mitigate risks.
The framework discusses the types of harms that may arise from the use of AI, the challenges in managing AI risks such as risk measurement and risk tolerance, the characteristics of trustworthy AI systems, and ways of profiling AI risks.
The NIST AI RMF also contains four core functions which are GOVERN, MAP, MEASURE, and MANAGE. Together, these functions provide a structure for AI risk management processes, help establish context for the accurate identification of AI risks, set up mechanisms for analyzing and tracking identified AI risks and related impacts, and guide the prioritization and treatment of AI risks.
ISO/IEC 42001

The ISO 42001 standard provides organizations with guidelines on how to implement an artificial intelligence management system (AIMS), which consists of policies, procedures, and best practices for the use, development, and provision of AI systems.
It serves as a framework for responsible AI and treats the AI risk management process as a cycle. It also consists of mandatory requirements and controls such as the formulation of an AI policy, processes for impact assessment, information transparency, and third-party relationships.
Using the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model, ISO 42001 outlines the steps to execute, control, and continuously improve an AI management system. This involves identifying organizational context and stakeholders and developing an AI policy, operational deployment and implementation of controls, evaluation and audit, and constant improvement and corrective action.
Organizations that demonstrate compliance with these regulatory frameworks can obtain certification and verify their capacity for responsible AI development.
Real-world examples of responsible AI use
Several companies have already succeeded in putting responsible AI into practice and have produced AI-powered products and services in an ethical and meaningful way. Let’s take a look at some of them:
6clicks’ AI Charter
6clicks is a leading GRC software provider known for its unique multi-tenanted risk and compliance management platform. Since 2019, it has been innovating on the applications of AI in GRC and has pioneered Hailey, a generative AI engine custom-built for GRC.
Demonstrating its commitment to the ethical, trustworthy, and responsible use of AI, 6clicks has established an AI Charter to guide its continuous development of Hailey. It outlines Transparency, Privacy and Data Security, Bias Mitigation, Continuous Improvement, Human-Centered Design, and Ethical Use as its core principles.
It has also defined a Clear Understanding of AI, Governance Approach, Risk Assessment, Data Quality and Management, Policies and Procedures, AI System Life Cycle, and Monitoring and Reporting as its prerequisites for Hailey AI.
Through these principles, 6clicks believes that it can achieve its mission of safely deploying powerful AI systems while making a positive impact.







