What is a GRC framework?
A GRC framework, short for Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance framework, is a comprehensive system that organizations use to manage and mitigate risks, ensure compliance with laws and regulations, and align their operations with business objectives. It provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and addressing risks, while also incorporating governance practices and compliance requirements. A GRC framework helps organizations establish effective internal controls, implement risk management processes, and ensure adherence to industry standards and regulatory requirements. By integrating governance, risk management, and compliance into one cohesive framework, organizations can make informed decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and mitigate potential threats and risks effectively.
Benefits of GRC Framework
A GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) framework offers numerous benefits for organizations. Firstly, it helps in ensuring legal and regulatory compliance. By providing a structured approach to internal audits and risk assessments, organizations can identify and address compliance requirements and meet regulatory obligations effectively.
Secondly, a GRC framework improves risk management by providing a systematic process for identifying, assessing, and managing risks. It allows organizations to proactively mitigate risks and reduce the likelihood of potential threats such as cyber threats and security risks. The framework also helps in aligning risk management with business objectives and strategic decisions, enhancing overall risk visibility and enabling informed decisions.
Moreover, implementing a GRC framework enhances operating efficiency. It streamlines business processes, eliminates manual processes, and inculcates automation. This increases productivity, reduces duplication of efforts, and ensures consistency across the organization. By optimizing risk management processes, organizations can identify and address compliance issues promptly, reducing the impact of operational risks.
In addition, a GRC framework facilitates better decision-making. It provides a common language and a wide range of capabilities that enable key stakeholders, including the executive team, to assess business risks and performance more effectively. This supports strategic objectives and enables the organization to make informed decisions based on data-driven risk analysis and risk analytics.
Implementing a GRC framework instills confidence within the organization. It provides an integrated collection of capabilities to manage compliance, risk, and governance, ensuring that the organization operates in line with industry standards and best practices. With real-time monitoring, audit trails, and visibility into risks, organizations can address potential threats and respond rapidly, enhancing confidence among stakeholders.
Components of the GRC framework
A GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) framework consists of several key components that work together to ensure effective risk management and regulatory compliance within an organization. These components include internal audits, risk assessments, compliance requirements, and the integration of industry standards and best practices. The framework also encompasses various elements such as business objectives, enterprise risk management, and the identification and analysis of different types of risks. Additionally, the GRC framework involves the active participation of key stakeholders, the implementation of compliance policies and processes, and the utilization of real-time monitoring and audit trails. By integrating these components, organizations can achieve a holistic approach to GRC, improving operational efficiency, enabling informed decision-making, and instilling confidence among stakeholders.
Internal audits and risk assessments
Internal audits and risk assessments play a crucial role within a GRC (governance, risk management, and compliance) framework. These activities help organizations identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks in order to achieve their business objectives and comply with regulatory requirements.
Internal audits are systematic and independent evaluations of an organization's processes, controls, and compliance requirements. They provide an unbiased assessment of the effectiveness and efficiency of an organization's internal controls, risk management processes, and adherence to industry standards and regulatory compliance. By conducting internal audits, organizations can identify weaknesses in their operations and implement necessary improvements to mitigate risks and enhance performance.
On the other hand, risk assessments aid in evaluating the potential impact of identified risks. They help organizations prioritize risks and allocate resources appropriately to manage and mitigate them effectively. Risk assessments involve assessing a wide range of risks, such as operational risks, security risks, and third-party risks. By understanding the types of risk they face, organizations can make informed decisions to protect their assets, reputation, and financial stability.
In conducting internal audits and risk assessments, different departments within the organization play important roles. Internal audit departments are responsible for independently evaluating and reporting on the effectiveness of an organization's internal controls. Compliance teams ensure that the organization adheres to regulatory requirements and industry standards. Risk management professionals work to identify, assess, and mitigate risks across the business.
Learn more about the 6clicks solution for audit and assessment here.
Compliance requirements & regulatory compliance
Compliance requirements and regulatory compliance are essential components of a GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) framework. Compliance requirements refer to the rules, regulations, and standards that organizations must adhere to in order to operate legally and ethically in their industry. These requirements are established by regulatory bodies and industry governing bodies to ensure fair practices, consumer protection, data privacy, and other important aspects of business operations.
Regulatory compliance within the GRC framework is of utmost importance as it helps organizations maintain a strong reputation, avoid legal troubles, and build trust with stakeholders. By complying with industry regulations and standards, organizations demonstrate their commitment to principled performance and their ability to meet customer expectations.
Compliance management plays a vital role in addressing measures used to conform with these requirements. It involves the development and implementation of policies, procedures, and controls that ensure the organization's activities are in line with regulatory guidelines. Compliance management monitors and assesses the organization's adherence to these requirements through various measures.
Key components of a compliance management process include internal and external audits, security procedures and controls, compliance research, and compliance reporting. Internal audits are conducted within the organization to assess the effectiveness of controls and identify any compliance gaps or issues. External audits involve independent assessments by external experts to ensure compliance with industry regulations. Security procedures and controls are put in place to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access or breaches. Compliance research involves staying updated with regulatory changes and best practices. Compliance reporting involves documenting and communicating compliance efforts to internal and external stakeholders.
Explore how 6clicks helps businesses with regulatory compliance, policy and control automation.
Industry standards & business objectives
Industry standards and business objectives are crucial components of a GRC framework as they help organizations effectively manage risks and ensure compliance. Adhering to industry standards ensures that organizations meet regulatory requirements and maintain best practices within their respective industries. On the other hand, business objectives serve as a guide for organizations to achieve their strategic goals and drive their overall success.
Organizations need to align their business objectives with industry standards and regulations to achieve a robust GRC framework. This alignment ensures that the organization's activities are in line with regulatory guidelines and industry best practices. By doing so, organizations can mitigate risks and prevent non-compliance issues that may arise.
Key industry standards such as ISO 27001 for information security, ISO 9001 for quality management, and GDPR for data protection, among others, influence the business objectives of an organization. These standards set the benchmarks for organizations in terms of the processes they need to follow, the controls they need to implement, and the level of risk they need to address. Adhering to these standards not only ensures compliance but also enhances the organization's reputation and credibility in the industry.
In conclusion, industry standards and business objectives are indispensable in a GRC framework. Organizations must adhere to various industry standards and regulations while aligning their business objectives to effectively manage risks and ensure compliance. By doing so, organizations can meet regulatory requirements, mitigate risks, and achieve their strategic goals.
Enterprise risk management & compliance frameworks
Enterprise risk management (ERM) and compliance frameworks play a vital role in the implementation of a comprehensive GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) framework. These frameworks are designed to help organizations identify, assess, and manage risks, as well as ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
In the context of a GRC framework, ERM is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks that could impact an organization's ability to achieve its objectives. It enables organizations to take a proactive approach to risk management by providing visibility into potential threats and vulnerabilities. By implementing an ERM framework, organizations can effectively manage risks and make informed decisions to enhance performance and protect their reputation.
Compliance frameworks, on the other hand, provide organizations with a structured approach to meet regulatory requirements and industry standards. These frameworks establish guidelines and best practices for compliance management, ensuring that organizations follow the necessary rules and regulations in their operations. Commonly used compliance frameworks include ISO 31000 and Basel III, which provide organizations with a common language and methodology to manage risks and comply with regulatory requirements.
Some key components of an ERM framework include risk identification, risk analysis, and risk mitigation strategies. Risk identification involves identifying and documenting potential risks that could impact an organization's objectives. Risk analysis entails assessing the likelihood and impact of these risks to prioritize them accordingly. Risk mitigation strategies involve implementing controls and measures to reduce or eliminate the identified risks.
Explore the 6clicks solution for enterprise risk management.
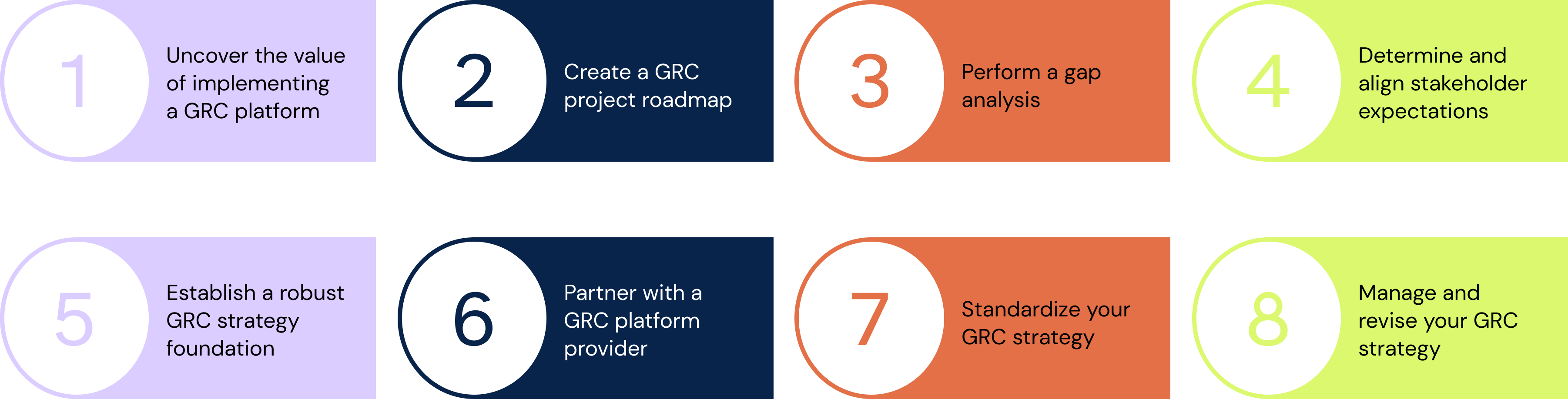
How to implement a GRC framework
Implementing a GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) framework is essential for organizations to effectively manage risks, ensure compliance with regulations, and achieve their business objectives. A GRC framework provides a structured approach to integrate governance, risk management, and compliance processes, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and enhance overall performance. By implementing a GRC framework, organizations can streamline their risk assessment and compliance management processes, establish clear communication channels with key stakeholders, and mitigate potential threats and vulnerabilities. This article will discuss how organizations can successfully implement a GRC framework, including key steps and considerations for effective implementation.
1. Uncover the value of implementing a GRC platform
Uncovering the value of implementing a GRC platform is essential for organizations seeking to strengthen their governance, risk management, and compliance strategies. By implementing a GRC platform, businesses can effectively identify existing strategies, remove unnecessary data and assets, prioritize profitable assets, and enhance their overall GRC strategy.
One of the primary benefits of a GRC platform is the ability to streamline and centralize various GRC processes. With a comprehensive platform in place, organizations can easily manage internal audits, risk assessments, compliance requirements, and regulatory compliance. By aligning these activities with industry standards, business objectives, and enterprise risk management, organizations can ensure that all lines of business and key stakeholders are working towards the same goals and objectives.
Moreover, a GRC platform provides a wide range of capabilities to manage risks effectively. From risk identification and assessment to security risks and third-party risks, the platform enables organizations to make informed decisions based on real-time data and insights. This integrated collection of capabilities allows businesses to gain visibility into risks and compliance issues, facilitating strategic decisions that align with their organizational structure and common language.
2. Create a GRC project roadmap
Creating a GRC project roadmap is an essential step in successfully implementing a Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) framework within an organization. The GRC project roadmap outlines the plan and timeline for implementing the framework and identifies key milestones, deliverables, and responsible parties throughout the process.
The first step in creating a GRC project roadmap is to define the scope and objectives of the project. This involves identifying the specific areas of the organization that will be included within the GRC framework and determining the desired outcomes. Additionally, it is crucial to align the scope and purpose of the GRC framework with the unique needs and requirements of each department. By involving key stakeholders from different departments in the planning phase, organizations can ensure that the GRC framework addresses their specific challenges and aligns with their strategic objectives.
Once the scope and objectives are defined, the next step is to determine the activities and tasks that need to be completed to implement the GRC framework. This includes conducting risk assessments, developing compliance policies and procedures, implementing control measures, and establishing reporting and monitoring mechanisms. Each task should be assigned to the appropriate team or individual, and a realistic timeline should be established for completing them.
A well-structured GRC project roadmap also includes regular checkpoints and audits to assess the progress and effectiveness of the framework. These checkpoints allow organizations to modify and adjust the roadmap if necessary, ensuring that the GRC framework evolves alongside the changing risk landscape and compliance requirements.
By creating a GRC project roadmap, organizations can effectively plan, implement, and monitor their GRC initiatives. This approach ensures that all departments are aligned, enabling better coordination and collaboration. Moreover, a well-executed GRC framework leads to improved risk management, enhanced compliance, and faster decision-making, ultimately benefiting the entire organization.
3. Perform a gap analysis
Performing a gap analysis is a crucial step in assessing the effectiveness of an existing GRC process and identifying areas for improvement. By collating relevant information on the current GRC process, organizations can gain insights into process maturity, data quality, and operational gaps.
The first aspect to evaluate is the process maturity. This involves analyzing the current GRC framework and determining the level of sophistication and integration with other business processes. By understanding the maturity level, organizations can identify gaps and opportunities for enhancement.
Next, the data quality should be assessed. This involves analyzing the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of the data being collected and utilized within the GRC process. Any issues with data quality can significantly impact the reliability and effectiveness of the framework.
Operational gaps should also be identified during the gap analysis. This involves examining the existing GRC processes and identifying any inefficiencies, duplication of efforts, or manual workflows that can be automated or eliminated. By addressing these gaps, organizations can streamline their GRC processes and improve overall efficiency.
Additionally, the gap analysis should emphasize the identification of any missing or duplicate data, which can lead to inaccuracies and gaps in risk assessments and compliance activities. By identifying and rectifying these issues, organizations can ensure the integrity and completeness of their GRC data.
4. Determine and align stakeholder expectations
Determining and aligning stakeholder expectations is a crucial step in implementing a GRC framework that spans across the entire organization. Stakeholders, including the executive team, business leaders, and key employees, play a vital role in driving the success of the framework.
Firstly, understanding stakeholder expectations helps organizations tailor their GRC framework to meet specific needs. By engaging with stakeholders, organizations can gain insights into their priorities, concerns, and compliance requirements. This enables the customization of the framework to align with various business objectives, industry standards, and regulatory requirements.
Secondly, executive team alignment is essential for effective implementation. Executives need to be on board, advocating for the GRC framework and driving its adoption throughout the organization. Their support and involvement ensure that the necessary resources, such as budget and manpower, are allocated for the implementation process.
Moreover, a top-down approach to change management is critical. Gaining executive approval ensures that the GRC framework receives the necessary buy-in and resources to succeed. Realistic change management processes, including creating a roadmap, defining clear roles and responsibilities, and setting realistic timelines, keep the implementation on track and minimize resistance.
Finally, establishing transparent communication channels facilitates the alignment of stakeholder expectations. Regular updates, feedback mechanisms, and open dialogue enable stakeholders to provide input, express concerns, and stay informed about the progress of the framework. This encourages their active involvement, trust, and commitment to the success of the GRC initiatives.
5. Establish a robust GRC strategy foundation
Establishing a robust GRC strategy foundation is crucial for organizations to effectively manage their risks, ensure compliance, and drive principled performance. This foundation serves as the fundamental framework that supports and guides all GRC initiatives within an organization.
One key aspect of establishing a solid GRC strategy foundation is the recognition of the dynamic cyber threat landscape. As technology continues to advance, cyber threats evolve at an alarming rate. Therefore, organizations must regularly assess and adapt their GRC strategies to address emerging cyber risks. This involves implementing proactive security measures, conducting regular risk assessments, and continuously monitoring and updating security controls.
Another important factor in building a strong GRC strategy foundation is the ability to address regulatory changes. Regulatory requirements and compliance standards are constantly evolving, and organizations must stay abreast of these changes to avoid penalties and reputational damage. By having a well-designed GRC framework in place, organizations can quickly identify and address any gaps in compliance and proactively implement necessary measures to meet regulatory requirements.
Laying the proper groundwork for a GRC strategy foundation enables organizations to align their processes, technologies, and people effectively. By integrating risk management, compliance, and performance management within a unified framework, organizations can achieve greater visibility into risks, make informed decisions, and consistently meet stakeholder expectations. This foundation provides the flexibility and adaptability needed to navigate the complexities of the business landscape and ensure long-term success.
6. Partner with a GRC platform provider
When implementing a GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) framework, partnering with a GRC platform provider can play a crucial role in ensuring success. A GRC platform provider offers specialized software solutions designed to streamline processes and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
One of the main benefits of using a GRC tool from a platform provider is the ability to centralize and automate various GRC processes. This can include risk assessments, compliance tracking, issue management, and reporting. By using a GRC tool, organizations can save time and resources by eliminating manual processes and increasing efficiency.
Another advantage of partnering with a GRC platform provider is the access to advanced automation capabilities. These capabilities can include workflow automation, notifications and alerts, and integration with other software systems. By automating GRC processes, organizations can reduce human error and ensure consistency in their compliance efforts.
When selecting a GRC platform provider, due diligence is essential. Organizations should consider factors such as ease of use, customization options, integration capabilities, and budget. It is important to choose a provider that aligns with the organization's unique needs and requirements.
Overall, partnering with a GRC platform provider can greatly enhance an organization's ability to effectively manage governance, risk, and compliance. By utilizing the features and capabilities of a GRC tool, organizations can streamline processes, improve compliance, and make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Check out the platform overview to understand the features and capabilities of 6clicks.
7. Standardize your GRC strategy
Standardizing your GRC strategy is a crucial step in ensuring the effectiveness and efficiency of your organization's governance, risk management, and compliance initiatives. By implementing industry standards such as NIST 800-53 or ISO 27001, you can establish a baseline for reference and align your GRC strategy with recognized best practices.
Having a standardized GRC strategy provides several benefits. Firstly, it enables your organization to meet compliance requirements more effectively. Industry standards outline specific control frameworks and security measures that address various risks and vulnerabilities. By adhering to these standards, you can demonstrate your commitment to maintaining a secure and compliant environment.
Additionally, standardizing your GRC strategy helps streamline and simplify your risk management efforts. It provides a common language and framework for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks across different lines of business. This consistency in approach allows for better collaboration among key stakeholders and facilitates informed decision-making.
Keeping detailed and dated records of GRC requirements is essential in maintaining compliance and demonstrating due diligence. These records serve as evidence of your organization's commitment to meeting industry standards and can be used for internal and external audits. Regular stakeholder meetings should review and update these records to ensure ongoing alignment with industry standards and evolving business needs.
In summary, standardizing your GRC strategy by implementing industry standards such as NIST 800-53 or ISO 27001 is essential to aligning your organization's efforts with recognized best practices. Doing so provides numerous benefits, including increased compliance effectiveness, streamlined risk management, and the ability to demonstrate due diligence through detailed and dated record-keeping.
8. Manage and revise your GRC strategy
Managing and revising your GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) strategy is crucial in ensuring that it remains aligned with your evolving business objectives and requirements. As your organization grows and changes, so do the risks and compliance challenges it faces. Adapting your GRC strategy accordingly helps you stay ahead of these challenges and maintain a secure and compliant environment.
One key aspect of managing your GRC strategy is the need to maintain detailed records of GRC requirements. These records serve as a vital reference point and ensure that your organization stays on track with meeting compliance obligations. By documenting and tracking GRC requirements, you can easily identify any key changes or updates that may impact your strategy.
Regular stakeholder meetings play a significant role in managing and revising your GRC strategy. These meetings facilitate open communication and collaboration among key stakeholders, enabling a holistic understanding of the organization's GRC needs. They provide an opportunity to review and update GRC records, ensuring ongoing alignment with evolving business objectives and requirements.
Annual audits are another critical component of GRC strategy management. Conducting regular audits helps you evaluate the effectiveness of your GRC controls and processes. It allows you to identify any weaknesses or areas that need improvement, guiding you in making informed decisions to enhance your organization's compliance posture.
Prioritizing compliance issues for remediation is also essential in managing and revising your GRC strategy. By categorizing and prioritizing compliance issues based on their impact and severity, you can allocate resources and focus on remediating high-priority risks. This approach ensures that your organization is addressing the most significant compliance challenges, reducing exposure to potential vulnerabilities.
Written by Anthony Stevens
Ant Stevens is a luminary in the enterprise software industry, renowned as the CEO and Founder of 6clicks, where he spearheads the integration of artificial intelligence into their cybersecurity, risk and compliance platform. Ant has been instrumental developing software to support advisor and MSPs. Away from the complexities of cybersecurity and AI, Ant revels in the simplicity of nature. An avid camper, he cherishes time spent in the great outdoors with his family and beloved dog, Jack, exploring serene landscapes and disconnecting from the digital tether.