The GRC buyer’s guide for 2025: Building resilience with AI-powered, federated solutions
Discover the ultimate GRC buyer's guide for 2025! Uncover how AI-powered, federated solutions transform compliance and security management for industries like government, aerospace, banking, and more. Learn about centralized control, continuous compliance, and advanced cyber GRC capabilities. Download now!
-1.png?width=200&height=249&name=Group%20193%20(1)-1.png)
The GRC buyer’s guide for 2025: Building resilience with AI-powered, federated solutions
What is the NIST certification process?
The NIST certification process is a framework that helps organizations and individuals demonstrate compliance with NIST security standards. NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) provides guidelines for developing effective cybersecurity programs but does not issue certifications directly. The process includes risk assessments, security controls, audits, and documenting policies to ensure proper cybersecurity practices. Achieving NIST certification shows a commitment to strong cybersecurity and risk management.
Who can get NIST certified?
- Federal agencies: These agencies must meet NIST security standards to protect national security data, often requiring advanced security measures, audits, and a comprehensive framework.
- Department of Defense (DoD): DoD contractors must adhere to the DFARS and NIST SP 800-171 to secure controlled unclassified information (CUI).
- Academic organizations: Universities and research institutions follow NIST’s cybersecurity frameworks to secure sensitive data and systems, often to qualify for government funding.
- Non-federal organizations and NGOs: Private and non-profit organizations also benefit from certification by aligning their security practices with NIST standards, ensuring they are eligible for government contracts and grants.
Key components of NIST certification
The NIST certification process involves several critical components, each designed to ensure that organizations meet the highest standards for cybersecurity and information protection. These include the implementation of comprehensive security programs, adherence to NIST guidelines, and continuous evaluation and improvement of security measures. Below are the key components in more detail:
1. Security programs & requirements: Organizations seeking NIST certification must meet specific security program requirements outlined by NIST. These requirements focus on implementing a security framework, regularly assessing risks, and securing information systems through various controls. The core elements of a NIST-compliant security program include:
- Risk assessments: Identifying vulnerabilities, threats, and the potential impact of security incidents.
- Security controls: Implementing technical, physical, and administrative controls to protect information systems, such as firewalls, encryption, and access management.
- Regular audits: Conducting internal and external audits to evaluate the effectiveness of security controls and ensure compliance.
- Documentation: Developing and maintaining security policies, procedures, and guidelines that align with NIST standards.
2. Controlling Unclassified Information (CUI): CUI refers to information that requires safeguarding but is not classified as secret or top secret. Organizations must adhere to specific guidelines for the protection of CUI, such as:
- Access control: Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, role-based access, and multi-factor authentication to restrict access to sensitive information.
- Data encryption: Encrypting CUI both at rest and in transit to ensure it cannot be accessed or intercepted by unauthorized parties.
- Incident response: Developing and testing an incident response plan to detect, report, and recover from any breach involving CUI.
3. Government Information Technology Security (GITS): GITS covers the security programs required by federal agencies and contractors to safeguard sensitive government information systems. Achieving compliance with GITS standards ensures the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of government IT systems. Key aspects of GITS include:
- Security posture: Ensuring all information systems are resilient to cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
- Compliance with NIST frameworks: Adhering to NIST cybersecurity frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) or NIST SP 800-53, which provide comprehensive guidance on securing federal information systems.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitoring information systems for security vulnerabilities, unauthorized access, or other incidents, and taking corrective action as necessary.
4. Security Controls and Standard: The NIST certification process involves following detailed security controls, many of which are described in NIST SP 800-53 and NIST SP 800-171. These controls provide a robust framework for organizations to secure their systems and data. Key areas covered include:
- Access control: Ensuring only authorized users can access certain systems or information.
- Incident response and recovery: Establishing processes to quickly respond to and recover from security incidents.
- System integrity and monitoring: Ensuring that systems are free from malware and vulnerabilities and are continuously monitored for security issues.
- Data protection: Implementing encryption, backup, and storage procedures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or loss.
5. Ongoing evaluation and improvement: NIST certification is not a one-time achievement; it involves ongoing evaluation and improvement of security measures. This includes:
- Continuous improvement: Updating security programs, policies, and procedures to address emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and changes in technology.
- Self-assessment and audits: Regular self-assessments and third-party audits to ensure continued compliance with NIST standards and to identify any security gaps.
- Training and awareness: Providing continuous training for staff and contractors to ensure they are aware of evolving security risks and best practices.
6. Alignment with NIST cybersecurity framework: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) outlines five core functions for managing and improving cybersecurity risk:
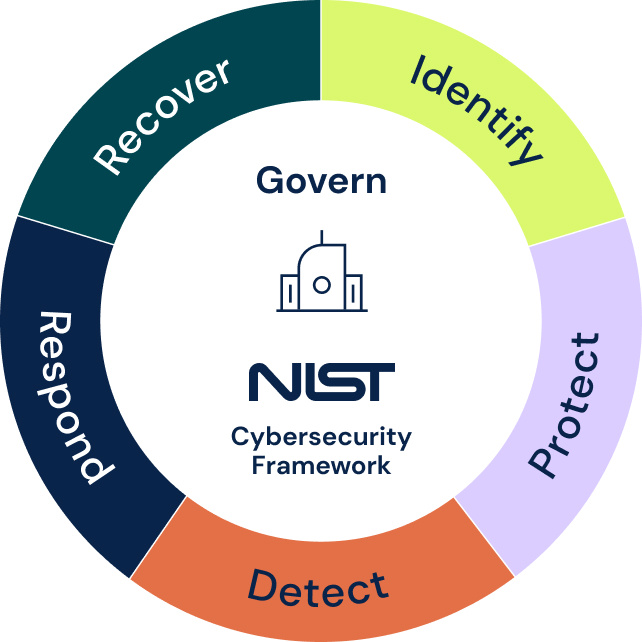
- Identify: Understanding the organization’s cybersecurity risks to systems, assets, data, and capabilities.
- Protect: Implementing measures to safeguard critical infrastructure and sensitive data.
- Detect: Identifying cybersecurity events in real-time.
- Respond: Responding to detected cybersecurity incidents to limit damage.
- Recover: Developing and implementing processes to restore capabilities and services after a cybersecurity event.
By following these core components and aligning with NIST’s frameworks, organizations not only secure their systems but also demonstrate their ability to manage cybersecurity risks effectively and comply with government standards.
Summary
The NIST certification process helps organizations demonstrate compliance with NIST’s cybersecurity standards. While NIST doesn’t directly issue certifications, it provides guidelines for risk assessments, security controls, audits, and documentation to ensure robust cybersecurity practices. Achieving certification indicates a strong commitment to securing information systems and managing cybersecurity risks.
Federal agencies, academic institutions, and private organizations can pursue NIST certification to enhance their security and meet industry standards. It is particularly crucial for federal contractors and organizations handling sensitive data. NIST certification ensures compliance with national standards and helps organizations qualify for government contracts and funding.









